Long-Join Intelligent Lighting Control System UM9900: Introduction To The JL-246CG And JL-245CZ Centralized Control Solution
Introduce
Long-Join’s UM9900 smart lighting system uses two main devices. One is the JL-246CG master controller, and the other is the JL-245CZ controller device. Together, they create one central mesh system for street lights. It now serves cities, parks, campuses, and industrial areas.
The system uses a Zigbee mesh network, supports wide-area lighting control, and connects easily with photocontrol, NEMA socket, and Zhaga socket ecosystems. With this article, we will walk through the architecture in a simple question-and-answer format, so that technical teams, city engineers, and integrators can quickly understand how UM9900 works and where it fits in a modern smart city lighting plan.

What Problem Does The UM9900 System Actually Solve In City Lighting?
Many cities still rely on traditional cabinet timers or standalone photocell switches. Once installed, those systems are hard to monitor, slow to adjust, and expensive to maintain. When one feeder trips or a manual setting is wrong, whole streets stay dark or over-lit, and teams often only discover issues after citizens complain.
UM9900 tackles these problems by giving you:
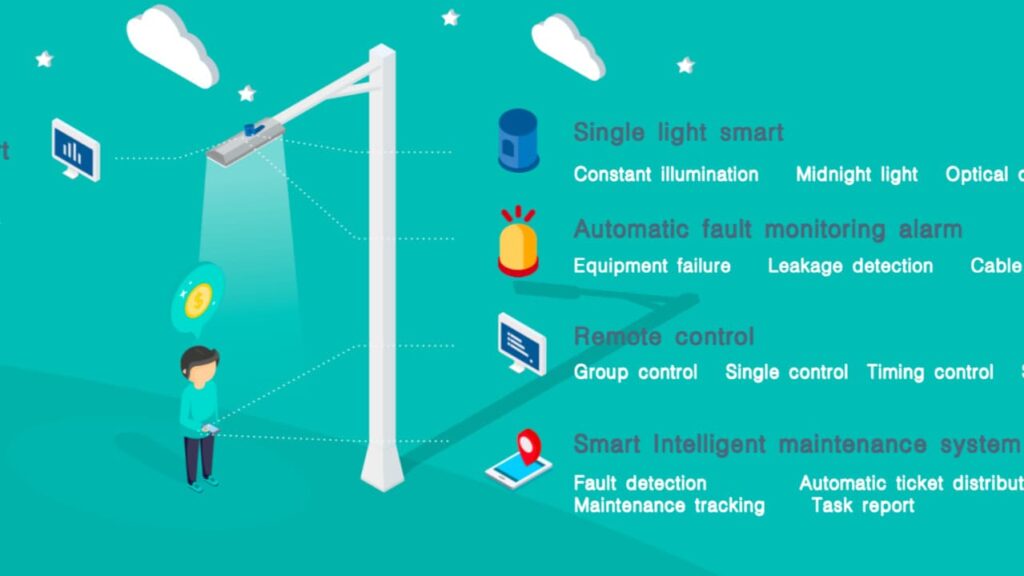
- Remote visibilityfor every pole-level street light controller
- Fine-grained dimming and scheduling, not just simple on/off
- Redundant mesh communicationbetween poles, so one failure does not break the whole line
- A unified web platform where you monitor energy, alarms, and field devices in real time
From a city-operations view, UM9900 works like a central nervous system for outdoor lighting: field controllers collect data and execute commands, while the JL-246CG master plus the UM9900 web platform coordinate the whole network.
UM9900 At A Glance
Item | What It Means In Daily Operation |
UM9900 platform | Web-based control center for all lighting projects |
JL-246CG master controller | Main controller intelligent lighting node managing groups/scenes |
JL-245CZ slave controllers | Pole-level smart remote control switch units for each luminaire |
Communication | Zigbee mesh; can be extended with LTE/NB-IoT where needed |
Typical applications | City streets, parks, campuses, industrial estates, communities |
The whole system uses open parts that work well in the field. It can grow with your smart city plans, not trap you in one small use.
How Do The JL-246CG Master And JL-245CZ Slave Controllers Work Together?
If you are new to smart lighting, it’s easy to get lost in part numbers. So let’s put the two core devices in simple language.
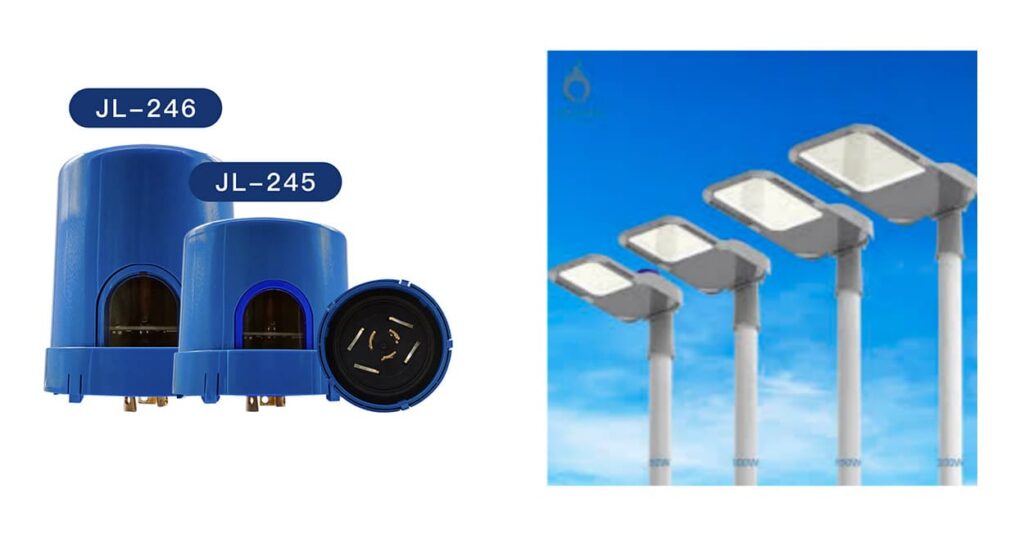
- JL-246CGis the “brain” on the pole: a NEMA-interface smart street light controller that talks to the UM9900 platform and manages downstream devices or scenes.
- JL-245CZis the “hands” at each luminaire: a twist-lock street light controller that actually switches and dims one light, measuring local conditions and sending data upstream.
Both units integrate photo sensor capability and Zigbee communication, so they can operate in dusk-to-dawn mode, follow central schedules, or blend both. This is especially useful when you combine UM9900 with Long-Join’s photocell control and twist-lock photocontrol series for layered lighting strategies.
Roles Of JL-246CG vs JL-245CZ
Feature / Function | JL-246CG Master Controller | JL-245CZ Slave Controller |
Primary role | Central node in the pole’s control hierarchy | Pole-level lamp or small group controller |
Interface | NEMA twist-lock NEMA socket on the luminaire head | Twist-lock interface or retrofit on existing fixtures |
Communication | Zigbee + optional LTE / NB-IoT uplink | Zigbee mesh node relaying data through the network |
Local sensing | Ambient light, electrical parameters | Ambient light, load status, basic metering |
Typical use | Group / scene controller for one smart pole | Individual lighting control for each lamp |
Integration with photocell products | Coordinates with Long-Join photocell lighting sensor families through UM9900 | Operates like an intelligent photocell for street light |
This division makes it easy to scale: you add more JL-245CZ slaves as you extend the line, while keeping a consistent architecture around a few JL-246CG master points.

How Does Centralized Control Improve Daily Operation And Maintenance?
For many maintenance teams, the worst part is this. They don’t know what’s wrong on site until someone complains there. UM9900 changes that by turning every controller into a small data point.
Through the UM9900 web platform, operators can:
- See live voltage, current, power factor, and cumulative energy for each node
- Adjust dimming levels, switching thresholds, and schedules remotely
- Group luminaires into scenes (e.g., “evening peak,” “late night economy mode”)
- Receive alarms for lamp failure, abnormal power, or communication loss
This is more than “nice to have.” Smart regulation frameworks and academic studies highlight that real-time monitoring and analytics are key to optimizing street lighting in modern cities.
Typical UM9900 Central Functions
Function | What The Operator Sees / Does |
Real-time map (GIS) | Location and status of every street light controller on one map |
State ratio dashboards | Share of lights on, off, in fault, or under maintenance |
Central dimming & scenes | 0–100% dimming per group or schedule, including midnight dimming |
Threshold setting for light sensor | Remote configuration of 20–100 lux switching threshold |
Remote updates | Firmware upgrade and parameter reset over the air |
For cities already using photocell street light products from Long-Join, UM9900 adds an extra layer: you keep the automatic dusk-to-dawn photocell behavior at the edge, but gain central override and analytics. This layered control is especially useful when integrating photocontrol receptacle hardware, such as Long-Join’s ANSI C136.41 NEMA 7-pin receptacles.
How Does The System Work With Photocells, NEMA Sockets, And Zhaga Sockets?
Many lighting projects today already use photocell for street light control through NEMA or Zhaga interfaces. The question is: can UM9900 work with what you already have?
Long-Join designs the UM9900 ecosystem to stay compatible with its own twist-lock photocontrols, photocontrol receptacles, and Zhaga socket products. This means:
- Existing luminaires with NEMA 7-pin sockets can host JL-246CG or separate photocell lighting sensor
- New designs using Zhaga Book 18 can integrate compact controller intelligent lightingmodules through products like JL-700 Zhaga socket.
Interface Options Around UM9900
Interface Type | Example Long-Join Product | What It Enables |
NEMA 7-pin receptacle | Pluggable photocell control, smart controllers, or shorting caps | |
Twist-lock photocontrol | Dusk-to-dawn photocell switch with surge protection | |
Zhaga socket | Low-profile interface for Zhaga-ready smart controllers |
By combining UM9900 with these hardware families, cities can roll out outdoor photocell light sensor strategies now and still remain ready for future smart nodes, sensors, or communication upgrades.
In Which Scenarios Does UM9900 Deliver The Most Value, And How Does It Scale?
Smart lighting is not the same. For all. It is a smart photocell-style controller that sits on top of the light. It talks to field nodes and sends data up to the cloud. UM9900 is designed to cover this spectrum without forcing different platforms for each type of project.
Typical scenarios include:
- City main roads and highways: use group-based dimming, traffic-driven scenes, and strict alarm handling.
- Residential communities and campuses: emphasize safety, softer dimming curves, and integration with CCTV or emergency buttons.
- Parks and greenways: combine motion sensing, environmental data, and reduced night-time light pollution.
Scaling is straightforward:
- Start with one district: a few JL-246CG masters and dozens of JL-245CZ slaves.
- Add more poles and controllers as new streets or parks are upgraded.
- Extend with new sensors or smart city functions without changing the backbone.
Scenario vs Configuration Example
Scenario Type | Typical Node Density | Key UM9900 Features Used |
Main urban road | 1 pole every 25–40 m | Central dimming, failure alarms, GIS monitoring |
Residential community | Short streets, mixed pole spacing | Scene-based scheduling, motion + light sensor |
Industrial / logistics | Large lots, high mast lights | Power quality tracking, midnight energy saving |
Parks & waterfronts | Curved paths, trees blocking direct lines | Mesh routing, adaptive dimming, sensor add-ons |
Because UM9900 uses web-based management and standard wireless protocols, it fits easily into broader smart-city programs targeting CO₂ reduction and improved public safety.
Conclusion
The Long-Join UM9900 intelligent lighting control system brings together the JL-246CG master controller and JL-245CZ slave controllers to create a robust, Zigbee-based centralized control solution for modern outdoor lighting.
With a self-healing mesh network, rich web dashboards, and compatibility with Long-Join’s photocontrol, NEMA socket, and Zhaga socket product families, it gives cities a practical path from simple dusk-to-dawn operation to full smart-city lighting.
For municipalities, EPC providers, and lighting manufacturers photocell partners looking to cut energy use, simplify operations, and prepare for future smart services, UM9900 offers a clear, scalable route forward—without throwing away the systems and photocell hardware you already trust.
External Links:
●https://www.digi.com/solutions/by-technology/zigbee-wireless-standard
●https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mesh_networking
●https://www.researchgate.net/publication/364583427_The_Potential_of_using_ZigBee_Technology_
to_Improve_the_Effectiveness_of_Smart_Street_Lighting_SystemsSSLS
●https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S2210670721002006




