What Is the Difference Between Photocell and a Motion Sensor?
Introduction
If you’re looking for a reliable source of light for your building that will not only save energy but also work on its own without manual monitoring then photocells and sensors will be your go-to choices.
But how to select the right device for your unique building?
In today’s article, we’ll be addressing this very question. So let’s dive deeper to learn what a photocell and motion sensor are and what are the pros and cons of using them.
What is a Photocell?

A photocell light sensor is a tiny gadget with a resistor, electrodes, and a transparent cover on the front. It employs light to regulate the flow of electrical current. Although photocells exist in a variety of configurations, they are always driven by the identical semiconductor technology that regulates electric current.
The working system of photocell
Semiconductors are regarded as the brains of today’s electronics. They are critical components that enable advancements in connection, computing, healthcare, the military, transportation, clean energy, and other fields. Semiconductors do not typically carry electricity, but when subjected to enough light, an electric current is formed.
Types and Uses of photocells
Photocells are commonly used to regulate parking lot lights, streetlights, and lit company signs. There are many different types of photocells available, but we’ll focus on those that are most useful for indoor and outdoor illumination. Plug-in photocells work with a regular outlet and require a pass-through plug. They are the easiest technique to regulate the operation of a single bulb.
Lamp base photocells attach to a light bulb socket, converting almost any light source (lamps, permanent fixtures indoors and outdoors) into an autonomous lighting system. This is an amazing photocell sensor for your home’s exterior lights when linked to a light switch.
Line-voltage photocells control the entire electrical circuit. This sort of photocell is ideal for monitoring security or landscape lighting. If you combine exterior lighting sensors with timers that regulate indoor illumination, you can deter attackers by providing the idea that someone is home.
Common type of photocells: The Dawn Light Sensor
The most typical application for photocells is dusk to dawn lighting, which activates landscape or general outdoor lighting at sunset and turns it off at daylight. Photocells with a line voltage are required for this. One advantage of utilizing a photocell sensor for dusk to dawn lighting is that you do not require a timer. They simply adjust to natural light, including seasonal variations.

Pros and Cons of photocells
Photocell light sensors are generally useful. But in real terms, there are a few drawbacks too.
Their advantages include the inexpensive cost. They are a long-term investment and reliable gadgets with a wide sensing range and fast response time.
Their disadvantage is that the clear cover becomes dirty over time, reducing sensor sensitivity. Longer-lasting lights are substantially more expensive, and photocells lack additional controls.
Motion Sensors
Photocells and motion sensors behave differently when it comes to turning on lights. Photocells sense variations in light intensity and respond accordingly. Motion sensors detect any physical movement throughout their range. Motion sensors can operate in one of two ways:
Active sensors produce light or ultrasonic sounds. They are engaged when one of these signals indicates a movement to the sensor. Depending on its range, the motion sensor may be able to recognize motion around corners. Passive sensors use infrared detection. They detect infrared energy released by warm things like animals or people and respond when these warm areas move.
Working system of motion sensors
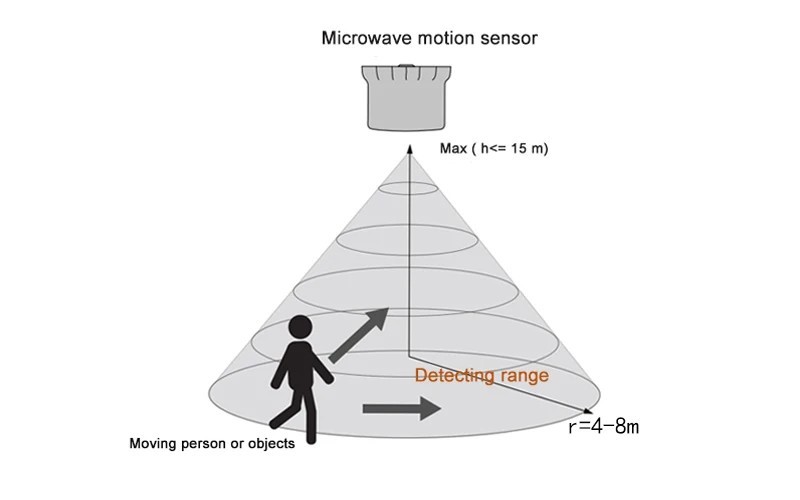
Motion sensor lights are used in a variety of applications. You’ve likely seen them countless times, whether business or residential. Motion sensors are used to enhance security systems, produce a hands-free lighting solution (for example, when you enter the foyer with your arms too full to turn on the lights), provide energy-efficient lighting in commercial buildings, and more. An important issue for motion sensors is how you may customize the controls to meet your needs. There are usually two types of motion sensor light controllers available. Sensitivity control allows the user to specify the amount of motion required to trigger the sensor. This is important because you want a person entering the room to activate the lights, not a bug. Time delay control allows the user to specify how long the lights remain on after the sensor is triggered and no further motion is recognized. Some motion sensors have a slider to adjust the range of the area they detect, allowing you to cover your driveway and sidewalk while avoiding motion from tree branches or streets.

(Check out our top-notch Luminaire Controller Zhaga Sensor with Microwave Motion for Street Light here)
Pros and Cons of motion sensors
Motion sensors for lights function to make life easier. Since they were made to be helpful, the advantages are more obvious than the disadvantages. Let’s explore the pros and cons:
The advantages of motion sensor lights are their energy efficiency and simple installation process. They are continents and offer more control. Their lifespan is also ideal for long-term usage.
The disadvantages are their temperature sensitivity and the issue of false triggers. And top quality lights that have a longer lifespan cost a lot more.
LED Compatibility of motion sensors
LED lights are popular due to their low cost and high energy efficiency. Although LED bulbs can be combined with photocells, they operate at such a low voltage that they necessitate an entirely different photocell type than a traditional bulb. Motion sensors can also be used with LED lights, but only LED bulbs, for additional cost savings, energy efficiency, and other advantages.
Still confused about which of these two is better for your building?
If yes, then your problem ends here. At Shanghai Longjoin we have got a team I’d experts who are always ready to guide you in the right direction, so contact us here and figure out the best lighting choice for your building.
Conclusion
In conclusion, choosing between photocells and motion sensors for lighting in your building depends on your specific needs and preferences. Photocells excel in providing cost-effective, reliable, and long-term solutions with a wide sensing range. The dusk-to-dawn application, in particular, eliminates the need for additional timers.
On the other hand, motion sensors offer energy-efficient and convenient lighting, especially with customizable controls like sensitivity and time delay. However, they may be sensitive to temperature changes and face occasional false triggers, and higher quality, longer-lasting options come at a higher cost.
Ultimately, the decision between photocells and motion sensors depends on factors such as the intended use, environmental conditions, and budget constraints. It’s essential to weigh the pros and cons of each technology to make an informed choice that aligns with your building’s unique requirements.
External links:
- https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Photoelectric_sensor
- https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Motion_detector





